Apple files for — and is granted — lots of patents by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office. Many are for inventions that never see the light of day. However, you never can tell which ones will materialize in a real product, so here are today’s patent highlights:
Apple has been criticized for ignoring its professional users for such things as failing to update the “new” Mac Pro in years. However, a newly granted patent (number 9,390,160) for “annotation of movies” shows the company still has ideas for Final Cut Pro X, its pro-level videography software (thought he ideas could trickle down to the consumer-oriented iMovie, as well).
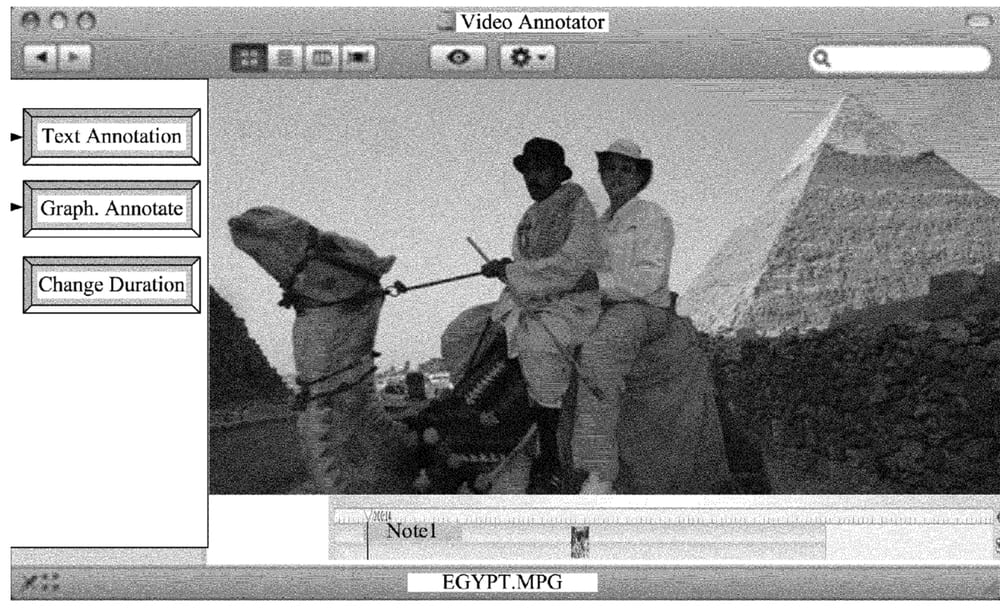
The patent involves a method of annotating a digital clip and setting a duration over which the annotation applies. The method provides a graphical user interface (GUI) with a display area for displaying the digital clip. The GUI provides controls for entering notes, including graphical notes, on the clip. The GUI also provides controls for setting the duration for which the annotation applies.
In some embodiments of the invention, a digital clip is played or otherwise presented to a user, and the user can enter annotation of the digital clip while it plays. Some embodiments pause the playing of a digital clip while annotations for the clip are entered.
Another granted patent (number 9,392,415) for “modeling connectivity of transit systems” shows that Apple wants to beef up the transit features of its Maps app on OS X and iOS. The invention involves methods, program products, and systems for using a “location fingerprint” database to determine a location of a mobile device (an iPhone, iPad, or, perhaps, a Mac laptop) are described. (Location fingerprinting is a technique for location sensing on 802.11 wireless local area networks.)
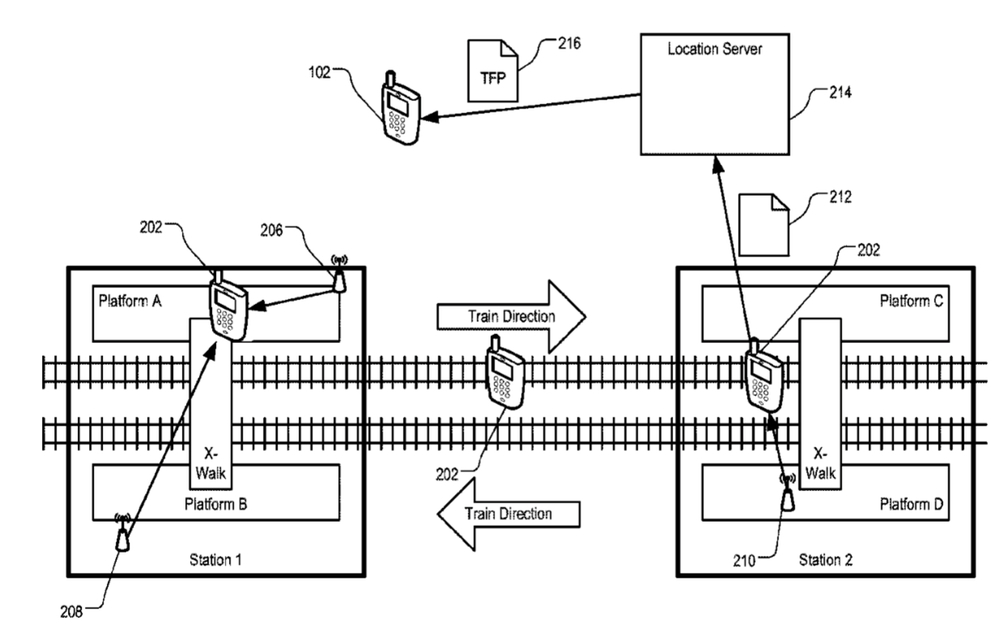
The device can use location fingerprint data received from a server to determine a location of the mobile device at the venue — such as inside a train traveling underground in a subway system. The device can obtain, from a sensor of the mobile device, a vector of sensor readings, each sensor reading can measure an environment variable — such as a signal received by the sensor from a signal source. The device can perform a statistical match between the vector and the location fingerprint data. The device can then estimate a current location of the mobile device based on the statistical match.
The transit system described in the patent can be a subway system including underground train stations and routes where location determination using GPS signals is difficult or impossible. A sampling device can measure signals, e.g., radio frequency (RF) signals detected at the stations or on the routes. A location server can construct a location fingerprint for each of the stations and the routes. Each location fingerprint can represent expected signal measurements by a user device if the user device is located at the respective station or route. The location server can provide the location fingerprint to a user device for the user device to determine a location of the user device within the station or on the route.
Get Rugged, Rock Solid Protection With iPad 2, 3, And 4 Cases And Accessories at OtterBox.com!
